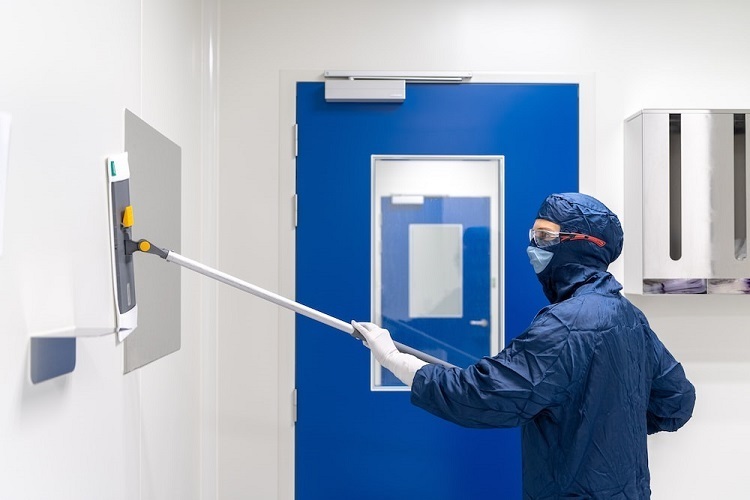
Manufacturing cleanrooms is a critical process with applications in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, electronics, and healthcare. It involves producing high-quality products under strictly controlled conditions to ensure they are free of contamination, particles, and other impurities.
According to Grand View Research, the global cleanroom technology market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2021 to 2028. However, manufacturing cleanrooms is not without challenges, which can impact the final product’s quality, efficiency, and safety.
This article discusses six of the most common challenges in cleanroom manufacturing and offers practical solutions. Whether you are a cleanroom manager or operator, understanding these challenges and how to address them will help you improve your manufacturing processes and deliver superior products.
Table of Contents
1. Contamination Control
Contamination control in cleanrooms is crucial to maintaining high product quality and ensuring personnel safety. Cleanroom manufacturing is done to maintain a highly controlled environment by regulating the number of particles in the air, controlling the temperature, humidity, and air pressure, and implementing strict protocols and procedures for personnel and material movement.
Cleanroom operators wear specialized clothing and use equipment such as air showers and HEPA filters to prevent particles into the environment. Regular cleaning and maintenance of equipment and surfaces are also critical in removing particles from the environment.
Cleanroom operators also monitor and document environmental conditions and air quality to ensure the environment remains within specified parameters. Overall, contamination control in cleanrooms requires a combination of advanced technology, rigorous protocols, and diligent personnel to maintain the integrity of the manufacturing process.
2. Maintaining Air Quality
Cleanroom professionals employ several techniques to overcome the challenge of making the air inside the cleanroom free of contaminants and particles. They use various techniques, including HEPA filters, to trap particles and maintain positive pressure inside the cleanroom to prevent the ingress of unfiltered air.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency states that HEPA filters have the potential to eliminate 99.97% of airborne particles, such as pollen, dust, bacteria, and mold, that are as small as 0.3 microns. Nevertheless, particles that are larger or smaller than this size are captured with even greater efficacy. This feature makes HEPA filters an effective tool for maintaining air quality in cleanrooms.
Additionally, cleanroom professionals wear specialized clothing to minimize the shedding of particles and move about the environment using specific protocols to avoid disturbing the air. Regularly monitoring environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure, is also done to maintain cleanroom air quality.
Cleanroom professionals employ advanced technology and strict protocols to maintain the integrity of the cleanroom environment and ensure high-quality product output.
3. Quality Control
Quality control in cleanrooms is critical to ensuring that the products manufactured in the environment meet the required specifications and are contamination-free. Cleanroom operators implement various measures to maintain quality control, such as monitoring environmental conditions, performing regular particle counts, and testing for microbial contamination.
They also perform visual inspections of the products and materials to detect any defects or abnormalities that may affect the quality of the final product. In addition, cleanroom professionals adhere to strict protocols and procedures for personnel and material movement to prevent cross-contamination and maintain product integrity.
Quality control in cleanrooms also involves regular calibration and maintenance of equipment to ensure that it functions correctly and meets the necessary standards.
4. Equipment Maintenance
Maintaining cleanroom equipment presents a significant challenge to cleanroom operators due to the potential risk of contamination. Cleanroom equipment must be calibrated and maintained regularly to ensure it meets the necessary standards and functions correctly. However, maintenance can introduce particles and contaminants into the environment, potentially compromising product quality.
Cleanroom operators must, therefore, perform maintenance procedures under controlled conditions, such as using special tools and equipment and performing maintenance in designated areas. They must also follow strict protocols and procedures for cleaning and disinfecting equipment after maintenance to prevent the introduction of contaminants.
5. Staff Training and Compliance
Cleanroom staff must understand the importance of maintaining a controlled environment and adhere to strict protocols to prevent contamination. In addition, they must receive thorough training on cleanroom procedures, including personnel and material movement, use of protective clothing and equipment, and proper handling and disposal of materials.
Compliance with these procedures is essential to maintaining a cleanroom environment, preventing contamination, and ensuring product quality. Cleanroom staff must also undergo regular training and testing to remain knowledgeable and compliant with evolving regulations and best practices.
Overall, staff training and compliance are essential components of a successful cleanroom environment, ensuring that personnel understand and adhere to procedures and maintaining a high level of quality control in the manufacturing process.
6. Cost Control
Cost control is a significant challenge in cleanrooms due to the substantial investment required to maintain a controlled environment. The construction and maintenance of cleanrooms can be costly, requiring specialized materials and equipment and implementing strict protocols and procedures.
According to Markets and Markets, the average cost of manufacturing a cleanroom ranges from $100 to $1000 per square foot. It can go even higher depending on the size of the room and the equipment used. Additionally, the cost of consumables, such as filters, cleaning supplies, and protective equipment, can add up quickly.
Cleanroom operators must balance the need for maintaining a controlled environment with the cost of doing so, seeking cost-effective solutions without compromising product quality or safety. It may involve the implementation of lean processes, the optimization of equipment usage, and the identification of more cost-effective materials and consumables.
Overall, cost control presents a significant challenge in cleanrooms, requiring careful planning and management to balance maintaining a controlled environment with the cost.
Conclusion
Cleanroom manufacturing presents several challenges that must be overcome to ensure product quality and personnel safety. Maintaining contamination control through air quality, equipment maintenance, and personnel training and compliance are critical components of a successful cleanroom environment.
Cost control also presents a significant challenge, requiring careful planning and management to balance the need for maintaining a controlled environment with the cost of doing so. However, by implementing best practices and evolving regulations, cleanroom operators can overcome these challenges and maintain a controlled environment that supports high-quality product output.
Through advanced technology, rigorous protocols, and diligent personnel, cleanrooms can continue to be a crucial component of modern manufacturing.